Multinomial classification
\[[x_1 x_2 x_3] \begin{bmatrix} w_{1} \\ w_{2} \\ w_{3} \end{bmatrix} = [w_1x_1+w_2x_2+w_3x_3]\] \[[x_1 x_2 x_3] \begin{bmatrix} w_{1} \\ w_{2} \\ w_{3} \end{bmatrix} = [w_1x_1+w_2x_2+w_3x_3]\] \[[x_1 x_2 x_3] \begin{bmatrix} w_{1} \\ w_{2} \\ w_{3} \end{bmatrix} = [w_1x_1+w_2x_2+w_3x_3]\]3번을 다 따로 계산하는 것은 번거롭다.
벡터의 곱 내적(Dot product)을 구하는 방법을 사용하자!
또 Logistic Regression에서 사용했던 것처럼 우리는 classify를 하고 싶기 때문에 \(\hat{y}\)의 값이 좀 더 이산적으로 나오길 원한다. 따라서 모든 \(\hat{y}\)에 대해 하나의 함수를 적용시켜주면 좋지 않을까?
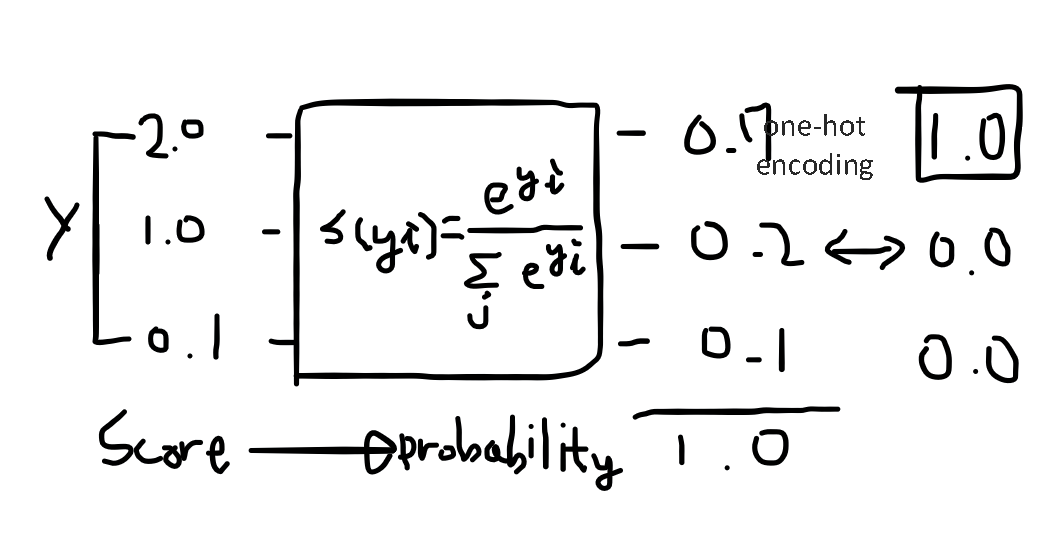
Cost function
\[\sum \log i(\hat{y_i})=\sum_iL_i\odot -\log(\hat{y_i})\]\(-\log(\hat{y_i})\) sigmoid 함수를 이용하기 때문에 \(\hat{y}\)가 y와 같을 때 비용은 0이 되고 \(\hat{y}\)가 y와 다를 때 비용은 무한히 커지게 된다.
이와 같은 cost function을 cross entropy라고 한다.
\[-\sum_i L_i log(S_i)\]응용하면
\[C(H(x),y) = -ylog(H(x)) - (1 - y)log(1 - H(x))\] \[-\sum_i L_i log(S_i) = -\sum_i L_i log(S_i) = \sum_i L_i \odot - \log(S_i)\]로지스틱 함수와 같은 역할을 한다고 볼 수 있다.
\[Loss = \frac{1}{N} \sum_i D(S(WX_i+b)L_i)\]import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
xy = np.loadtxt('train.txt', unpack=True, dtype='float32')
x_data = np.transpose(xy[0:3])
y_data = np.transpose(xy[3:])
#Input
X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 3])
Y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 3])
#Weights
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([3,3]))
#Our model
hypothesis = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X, W))
#minimize error using cross entropy
learning_rate = 0.001
#Cross entropy
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(Y * tf.log(hypothesis), reduction_indices=1))
#Gradient Descent
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Initialize
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#Launch graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for step in range(5001):
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X:x_data, Y:y_data})
if step % 1000 == 0:
print(step, sess.run(cost, feed_dict={X:x_data, Y:y_data}), sess.run(W))
print("\n")
a = sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X:[[1,11,7]]})
print(a,sess.run(tf.arg_max(a, 1)))
b = sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X:[[1,3,4]]})
print(a,sess.run(tf.arg_max(b, 1)))
c = sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X:[[1,1,0]]})
print(a,sess.run(tf.arg_max(c, 1)))
all = sess.run(hypothesis, feed_dict={X:[[1,11,7],[1,3,4],[1,1,0]]})
print(all, sess.run(tf.arg_max(all, 1)))
>>
0 1.09774 [[ -8.33333252e-05 4.16666626e-05 4.16666480e-05]
[ 1.66666694e-04 2.91666773e-04 -4.58333408e-04]
[ 1.66666636e-04 4.16666706e-04 -5.83333429e-04]]
1000 1.02354 [[-0.10928574 -0.02282181 0.13210757]
[ 0.02266254 -0.02678034 0.00411783]
[ 0.02685853 0.08210357 -0.10896212]]
2000 0.985988 [[-0.21581143 -0.05025396 0.26606542]
[ 0.02894915 -0.06228962 0.03334056]
[ 0.04230019 0.12409624 -0.16639642]]
3000 0.95411 [[-0.31725991 -0.07705297 0.39431274]
[ 0.0336593 -0.08655652 0.05289738]
[ 0.0584402 0.1547873 -0.21322735]]
4000 0.926335 [[-0.41402569 -0.10293558 0.51696134]
[ 0.03758517 -0.10280674 0.06522179]
[ 0.07442016 0.17733486 -0.25175497]]
5000 0.901696 [[-0.5065074 -0.12772508 0.63423264]
[ 0.04120506 -0.1133228 0.07211792]
[ 0.08978193 0.19396654 -0.2837483 ]]
[[ 0.53329509 0.2951085 0.17159635]] [0]
[[ 0.53329509 0.2951085 0.17159635]] [1]
[[ 0.53329509 0.2951085 0.17159635]] [2]
[[ 0.53329509 0.2951085 0.17159635]
[ 0.31603345 0.44044486 0.24352166]
[ 0.18252464 0.22840941 0.58906591]] [0 1 2]